How Qualitative Research and AI Enhance Product Analysis in Retail
Retail is constantly evolving. With the rise of digitalisation and increasing global competition, understanding consumers and adapting quickly to their needs has become crucial.
In this context, two tools stand out for their ability to generate valuable insights: qualitative research and artificial intelligence (AI). According to a survey conducted by Canva of over 1,300 IT sector leaders in 2024, 94% plan to increase investment in AI during this year.
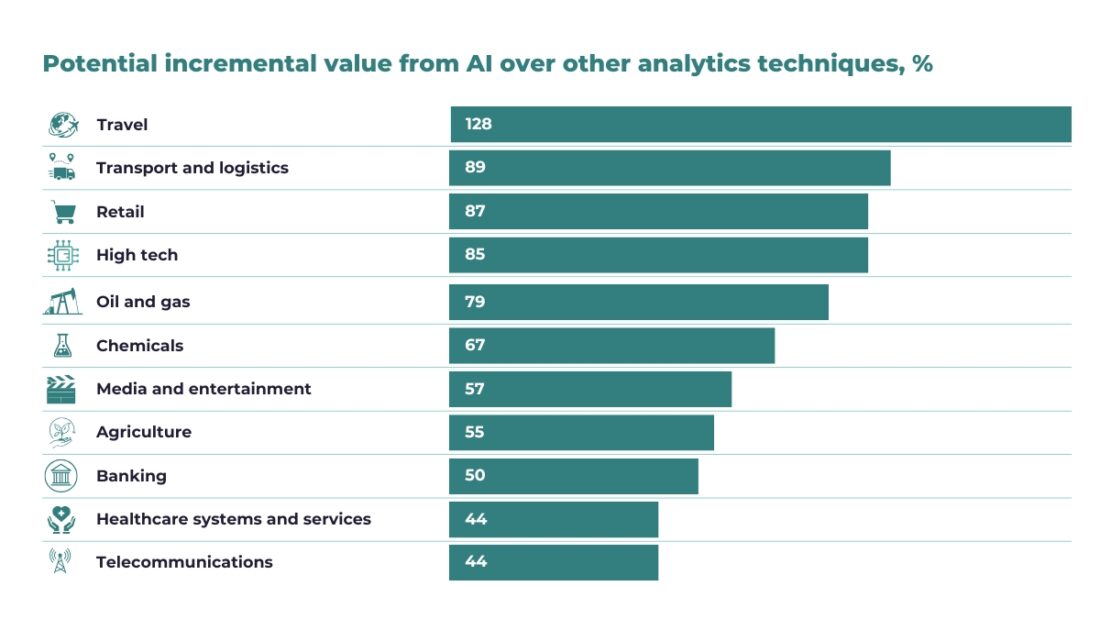
Furthermore, as can be seen in the chart below, in the retail sector there is an 87% incremental value of AI compared to other analytical techniques for studying markets and improving product analysis:
Source: McKinsey Global Institute analysis, February 2019
This article explores how these methodologies complement each other, improve analysis and strengthen the commercial strategies of retail businesses.
The Role of Qualitative Research in Retail: Key to Success
Qualitative Research Methods
Qualitative research is fundamental to understanding consumers from a deep and human perspective. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data, qualitative research is interested in the emotions, motivations and experiences behind customer behaviour.
Several key methods are used in retail:
- In-depth interviews: These face-to-face conversations allow exploration of the consumer’s perception and feelings about a product or service.
- Focus groups: These are group sessions where participants discuss and share opinions. They are especially useful for evaluating prototypes and marketing concepts or new product categories.
- Participatory observation: This method involves observing customers in their usual environments, such as physical stores or digital platforms. How shoppers interact with products, the areas they visit most or even the time they spend in certain aisles can offer key clues to optimizing the shopping experience.
- Content analysis: Examines texts and messages on digital media, such as comments on social media, product reviews or interactions on forums. This method helps identify recurring themes, widespread opinions and common perceptions.
Through these techniques, brands can obtain insights into the more subjective aspects of consumer behaviour, allowing them to understand not only the “what” of their choices but also the “why”.
Benefits of this Type of Research in Retail
Qualitative research provides a detailed picture of the consumer and, furthermore, drives better-informed strategic decisions.
Its key benefits include:
- Customer empathy: Helps brands understand not only what customers buy but why they buy it. For example, a customer may buy a product both for its functionality and because it reinforces their identity or values.
- Early trend detection: Listening directly to consumers allows for the identification of emerging trends, such as preferences for eco-friendly products or omnichannel shopping experiences.
- Adaptation to local markets: Each market has its own cultural, economic and social particularities. Qualitative research allows strategies to be adjusted to meet the specific needs of each region.
- Customer-centric product design: By identifying what really matters to consumers, companies can develop products that resonate better with their expectations.
How Retail Businesses Approach Market Research
Retail combines various strategies to gather relevant consumer data. Among the most prominent methodologies, qualitative research remains essential for complementing quantitative analysis.
Use of Focus Groups and Interviews
Focus groups allow companies to explore group perceptions, identify consensus and uncover ideas that would not emerge in individual interviews. For example, when launching a product, they can reveal how the design or functionality impacts the purchase decision.
On the other hand, individual interviews delve into personal experiences and generate a more complete understanding. This method is ideal for exploring sensitive topics, such as dissatisfaction with a product or the perception of high prices.
Ethnographic and Observational Studies
Ethnographic studies are particularly useful for observing behavioural patterns in natural settings. In retail, these studies allow you to discover how customers navigate a store, how they interact with products or what motivates them to choose one brand over another.
In digital environments, observation includes analyzing the user journey on e-commerce platforms. “Where do they abandon the basket? Which categories do they visit most frequently?” The answers to these questions are essential for optimizing both the design and functionality of online stores.
Social Media and Online Community Listening
The growing influence of social media makes these platforms an ideal space for qualitative research. Social listening tools allow for tracking mentions, hashtags and trends in real time, offering valuable perspective on how customers perceive a brand or product.
Online communities, such as specialized forums or review sites, are also sources of qualitative insights. For example, a technology brand can use these platforms to gather opinions on new devices or identify unmet needs.
Research Groups and Customized Panels
Customized panels are selected groups of consumers who participate in recurring studies. These initiatives allow data to be collected continuously and create a closer relationship with customers. Panels are ideal for product testing, advertising campaigns or improvements in customer service.
Use Cases of AI in Retail for Analyzing Products and Opinions
Artificial Intelligence has revolutionized retail by allowing for faster, more accurate and scalable analysis. Its applications range from product development to improving the customer experience.
1. Optimization in Product Development
AI can analyze historical data, market trends and consumer preferences to guide the design of new products. For example, machine learning algorithms can predict which features will be most valued by a specific segment of customers.
A notable example is the use of AI by fashion brands, which analyze purchasing patterns and trends to design collections that resonate with current preferences. Furthermore, thanks to the use of a real-time market analytics platform such as flipflow, they can also monitor what is happening across the entire market and what their competitors are doing. Our CEO, Ricardo García, detailed this functionality during an interview on RTVE’s Zoom Net programme, in which he discussed our collaboration with the Spanish fashion brand Mango.
2. Real-time Customer Insights
AI allows for the collection and analysis of real-time data, making it easier to detect problems or emerging trends almost instantly. For example, a market analytics platform powered by Artificial Intelligence can identify that negative reviews of a product are increasing due to quality issues, allowing for corrective action to be taken quickly.
On the other hand, sentiment analysis tools help brands understand how customers feel about a product or service on social media and other channels.
3. Customer Support and Feedback Analysis with AI
AI-powered chatbots not only improve the customer experience by quickly resolving queries but also generate valuable data. By analyzing these interactions, brands can identify frequently asked questions, areas for improvement and new opportunities.
For example, a retail brand may discover that many customers are asking about personalization options, which could guide the development of customized products.
Future Challenges and Trends
Ethical Considerations
The use of qualitative research and AI in retail brings with it ethical challenges that are essential to ensuring customer trust and the sustainability of strategies. According to the Canva survey mentioned at the beginning of this article, 72% of respondents acknowledged that the increase in investment in technological applications not only increases the complexity of their work but also the risks associated with security. These results reflect some of the main challenges facing businesses, including:
- Data privacy: With the increase in the collection of personal data, companies must ensure compliance with data regulations, such as GDPR in Europe.
- Bias in algorithms and qualitative analysis: Both AI and qualitative methods can be influenced by bias. Algorithms can amplify stereotypes if not trained with diverse data, while qualitative researchers must be aware of their own biases.
- Transparency and consent: It is crucial that consumers are clearly informed about how their data is collected and used. They should also have the option to control their participation in these processes.
Emerging Trends
The future of qualitative research and AI in retail is defined by technological innovation and the growing demand for personalized experiences. Some prominent trends include:
- Omnichannel and advanced personalization: The combination of data from multiple channels (physical and digital) with AI will allow for the creation of more cohesive and personalized shopping experiences, tailored to the needs and behaviours of each customer. In addition, platforms that combine qualitative and quantitative analyses automated through AI will streamline processes and reduce costs for those companies that implement them.
- Emotional AI: Tools capable of analyzing the customer’s emotional state during real-time interactions, allowing brands to adjust their responses and strategies in a more empathetic way.
- Sustainability and social responsibility: As consumers demand greater sustainability from brands, they must integrate environmental and social metrics into their research and analysis processes.
Conclusion: Towards a More Connected and Agile Retail Sector
The combination of qualitative research and artificial intelligence is redefining product analysis in retail. While qualitative research provides depth, context and a human perspective, AI amplifies the speed and accuracy of analysis, transforming data into actionable insights.
However, this advancement also brings with it ethical and strategic challenges that businesses must address carefully. Success will depend on brands’ ability to balance technological innovation with a customer-centric approach, respecting their privacy and building long-term trusting relationships.
Businesses that successfully integrate these tools will not only optimize their products and services but also ensure their relevance and leadership in the competitive world of retail.